Discover the marvels of graphene, a revolutionary material poised to transform electronics. Uncover its exceptional properties, potential applications, and ongoing challenges in this insightful exploration.
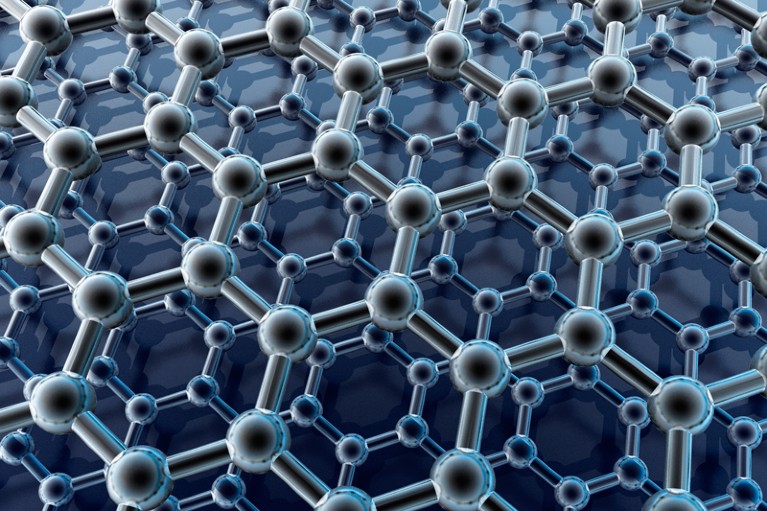
Graphene, a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, has sparked the imagination of scientists and engineers since its discovery in 2004. Regarded as a wonder material, graphene possesses extraordinary properties that have the potential to revolutionize diverse fields, including electronics, energy, and medicine. This blog post embarks on an exploration of the captivating world of graphene, shedding light on its exceptional properties, potential applications in electronics, and the challenges that must be addressed for its widespread integration.
Exceptional Properties of Graphene
Graphene's exceptional
properties position it as an ideal candidate for next-generation electronics:
A. High Electrical Conductivity:
Graphene boasts superior
electrical conductivity, surpassing even copper and silver. This conductivity
facilitates the creation of faster and more efficient electronic devices.
B. High Thermal Conductivity:
As an excellent
conductor of heat, graphene enables efficient heat dissipation from electronic
devices, potentially leading to smaller and more compact designs.
C. Mechanical Strength:
Remarkably strong and
lightweight, graphene's tensile strength is 200 times greater than that of
steel, making it ideal for flexible and durable electronics.
D. Optical Transparency:
Nearly transparent to
visible light, graphene holds promise for transparent electronics and
optoelectronics.
E. Large Surface Area:
Graphene's substantial surface area makes it suitable for applications such as sensors, batteries, and supercapacitors.
Potential Applications in Electronics
Graphene's unique
properties unlock a myriad of potential applications in electronics:
A. Transistors:
Graphene transistors
could outperform current silicon transistors, leading to faster and more
energy-efficient computers and mobile devices.
B. Touchscreens:
Transparent and flexible
touchscreens for smartphones, tablets, and other devices could be realized
through graphene technology.
C. Optoelectronics:
Graphene-based LEDs and
lasers hold the potential for enhanced efficiency and brightness compared to
existing devices.
D. Sensors:
Graphene's high surface
area and sensitivity make it ideal for various sensor applications, including
gas sensors, biosensors, and environmental sensors.
E. Energy Storage:
Graphene supercapacitors could revolutionize energy storage with significantly faster charging and discharging times, making them ideal for electric vehicles and renewable energy storage.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While graphene presents
immense potential, several challenges must be addressed for its widespread
adoption in electronics:
A. Scalable Production:
The current cost and
scalability of high-quality graphene production pose challenges for commercial
applications.
B. Doping:
Effectively doping
graphene, a process that alters electrical properties, remains a technical
challenge.
C. Integration with Existing Technologies:
Integrating graphene
with silicon-based technology presents significant technical hurdles that
researchers are actively addressing.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research and development efforts are making significant strides in addressing them, paving the way for graphene to play a transformative role in the future of electronics.
Conclusion
Graphene stands as a
revolutionary material with the potential to reshape the electronics landscape.
Its exceptional properties provide a glimpse into a future filled with faster
computers, more efficient energy solutions, and innovative electronic devices
that were once only imagined. While challenges persist, ongoing research
efforts are bringing us closer to realizing the incredible potential of graphene,
ushering in a new era of technological advancement.
Additional Resources
For further exploration,
consider these additional resources on graphene:
·
Graphene
for Physicists, Materials Scientists, and Engineers - Physics World
#GrapheneRevolution #MaterialsScience #ElectronicsInnovation #GrapheneApplications #FutureTechnology